Python Data Types
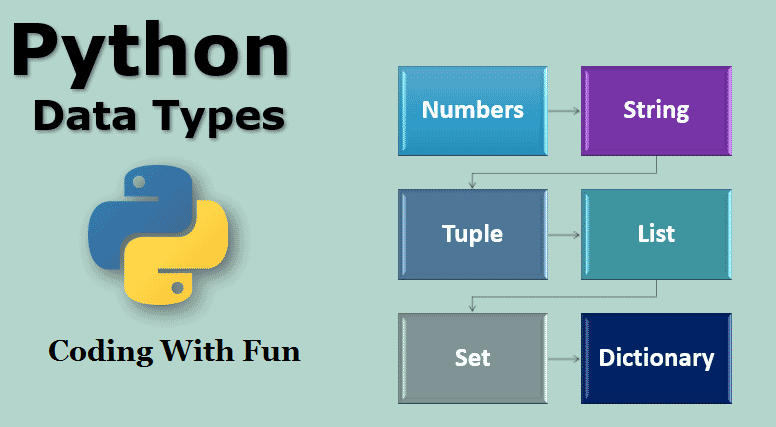
Built-in Data Types
In programming, statistics kind is an essential concept.
Variables can keep information of distinct types, and exclusive kinds can do exclusive things.
Python has the following statistics sorts built-in with the aid of default, in these categories:
Text Type: str
Numeric Types: int, float, complex
Sequence Types: list, tuple, range
Mapping Type: dict
Set Types: set, frozenset
Boolean Type: bool
Binary Types: bytes, bytearray, memoryview
Getting the Data Type
You can get the records kind of any object by means of the use of the type( ) function:Example:-
Print the information kind of the variable x:
x = 5
print(type(x))
Try it Yourself»»
Setting the Data Type
In Python, the statistics kind is set when you assign a price to a variable:
Example Data Type Try it
x = "Hello World" str Try it
Setting the Specific Data Type
If you desire to specify the information type, you can use the following constructor functions:
Example Data Type Try it
x = complex(1j) complicated Try it
x = list(("apple", "banana", "cherry")) list Try it
x = tuple(("apple", "banana", "cherry")) tuple Try it
x = range(6) range Try it
x = dict(name="John", age=36) dict Try it
x = set(("apple", "banana", "cherry")) set Try it
x = bool(5) bool Try it
x = bytes(5) bytes Try it
x = bytearray(5) bytearray Try it
x = memoryview(bytes(5)) memoryview Try it
Python Numbers
There are three numeric sorts in Python:
- int
- float
- complex
Variables of numeric kinds are created when you assign a fee to them:
Example:-
x = 1 # int
y = 2.8 # float
z = 1j # complex
To confirm the kind of any object in Python, use the type( ) function:
Example:-
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
Try it Yourself»»
Int, or integer, is a complete number, high-quality or negative, except decimals, of limitless length.
Example:-
Integers:
x = 1
y = 35656222554887711
z = -3255522
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
Int
Int, or integer, is a complete number, high-quality or negative, except decimals, of limitless length.
Example:-
Integers:
x = 1
y = 35656222554887711
z = -3255522
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
Try it Yourself»»
Example:-
Floats:
x = 1.10
y = 1.0
z = -35.59
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
Float
Float, or "floating factor number" is a number, high-quality or negative, containing one or extra decimals.Example:-
Floats:
x = 1.10
y = 1.0
z = -35.59
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
Try it Yourself»»
Float can additionally be scientific numbers with an "e" to point out the electricity of 10.
Example:-
Floats:
x = 35e3
y = 12E4
z = -87.7e100
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
Float can additionally be scientific numbers with an "e" to point out the electricity of 10.
Example:-
Floats:
x = 35e3
y = 12E4
z = -87.7e100
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
Try it Yourself»»
Example:-
Complex:
x = 3+5j
y = 5j
z = -5j
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
Complex
Complex numbers are written with a "j" as the imaginary part:Example:-
Complex:
x = 3+5j
y = 5j
z = -5j
print(type(x))
print(type(y))
print(type(z))
Try it Yourself»»
You can convert from one kind to some other with the int( ), float( ), and complex( ) methods:
Example:-
Convert from one kind to another:
x = 1 # int
y = 2.8 # float
z = 1j # complex
#convert from int to float:
a = float(x)
#convert from waft to int:
b = int(y)
#convert from int to complex:
c = complex(x)
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print(type(a))
print(type(b))
print(type(c))
Try it Yourself»»
Type Conversion
You can convert from one kind to some other with the int( ), float( ), and complex( ) methods:
Example:-
Convert from one kind to another:
x = 1 # int
y = 2.8 # float
z = 1j # complex
#convert from int to float:
a = float(x)
#convert from waft to int:
b = int(y)
#convert from int to complex:
c = complex(x)
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print(type(a))
print(type(b))
print(type(c))
Try it Yourself»»
Note: You can't convert complicated numbers into some other variety type.
Random Number
Python does no longer have a random( ) characteristic to make a random number, however Python has a built-in module referred to as random that can be used to make random numbers:
Example:-
Import the random module, and show a random wide variety between 1 and 9:
import random
print(random.randrange(1, 10))









0 Comments
If you are a good learner please leave a challenging question on comment box for us when you visited this website ( Coding with Fun).